Bit Tongue: Pain Treatment & Prevention
Table of Contents
- Why Do People Bite Their Tongue?
- Biting Your Tongue
- First Aid
- How Long to Heal?
- Repeatedly Biting
- Prevention
- Serious Injuries
A tongue bite is rarely life-threatening, but it is a painful injury that can affect your daily routines until it heals.
In most cases, biting your tongue is an accident. Not much can be done to prevent these incidents, although slowing down, reducing stress, and practicing more mindfulness may help.
If you’re repeatedly biting your tongue, there may be an underlying issue involved. Related conditions may include malocclusion (misaligned teeth or bite) or seizures.
You should consult a doctor about these recurring bites. Possible prevention methods might include wearing a mouth guard or tongue protector at night.
Most tongue bites won’t require treatment. If there’s minor bleeding or pain, you may treat the bite with some first aid tools (like a gauze pad) or pain reliever. If the tongue is badly injured and swelling or bleeding excessively, you should seek immediate emergency care.
While recovering from biting your tongue, be sure to practice good oral hygiene and monitor the area for any signs of infection, such as fever or swelling. If you suspect the tongue is infected, seek immediate emergency care.
Why Do People Bite Their Tongue?
Bites can occur accidentally as you eat, sleep, talk or fall as a result of an accident during physical activity. It can also happen if you are in a bicycle or car accident.If you bite your tongue once in a while, you might be able to resolve any pain and bleeding with time and simple self-care remedies at home. However, a deep tongue wound requires medical attention if it fails to heal on its own.If tongue bites happen to you a lot, it may be time to stop considering these bites accidents and look at a deeper problem to fix. You may have an underlying medical or dental issue (seizures or a misaligned bite, for example), and you should consider consulting a doctor or dentist for their opinions about the cause and suggestions for treatment.
Ways One Might Bite Their Tongue
Ultimately, one can bite their tongue at any time. It’s usually an accidental occurrence and very common.
You might bite your tongue while doing the following:
Eating and chewing
Speaking
Sleeping
Being involved in an accidental fall or crash
Having a seizure or medical emergency
Performing physical activity, such as exercises or moving an object
Experiencing stress or anxiety
Playing sports
Assessing the Severity of a Tongue Bite
Tongue bites can range from minor to severe. While minor to moderate bites generally won’t require medical care, severe bites need prompt medical attention.
Here are steps to take to assess the severity of a tongue bite:
1. View the wound. If the tongue has been bitten through or the bite appears deep, go to the emergency room or call 911. Stitches are likely required.
2. Consider the bleeding. If bleeding is intense or seems excessive, it needs to be assessed by a doctor.
3. Rinse the mouth. Use a lukewarm salt water rinse, and gently swish the mixture around the mouth. This will clean the area, so you can better assess it.
4. Apply light pressure. Use a sterile gauze to slow bleeding. If you are soaking through the gauze quickly and pressure isn’t helping, see a doctor promptly.
Using First Aid to Treat Tongue Bites
Cuts to the tongue can result in a range of issues you will need to deal with, starting with bleeding and pain, and ending with uncontrolled bleeding and infections.
Bleeding: A fresh tongue cut can bleed for several hours, but this is generally controllable. However, there are rare cases of excess, uncontrollable bleeding, especially from deep wounds.
Pain and soreness: This is usually the immediate effect of a bit tongue. Eating salty or spicy foods can aggravate the pain.
Swelling: Inflammation around the wound can occur.
Infection: This is a rare outcome that may be accompanied by fever and extreme pain.
Canker sores: Even if they are small, these lesions may be so painful that they make it difficult to talk, eat, drink or swallow.
You can ease pain and accelerate healing from a minor tongue bit with a few immediate self-care actions.
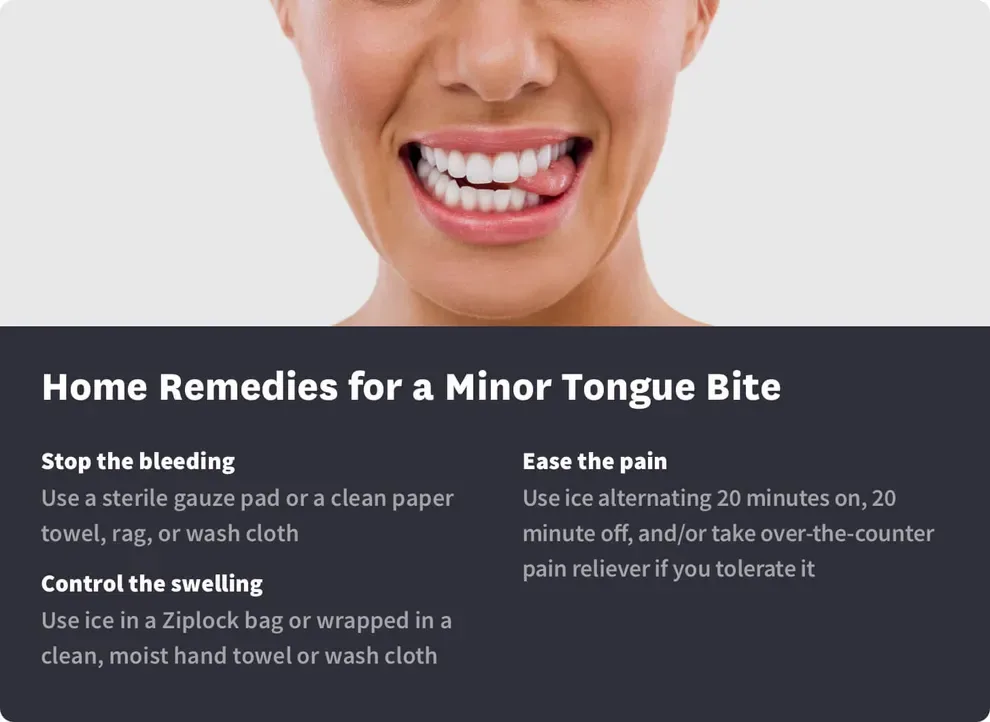
Stop the bleeding. Use a sterile gauze pad. If you don’t have a gauze pad, use a paper towel or a clean rag or washcloth. Put pressure on the bitten area for at least five minutes before checking to see if you’re still bleeding.
Control the swelling. Use an ice pack, ice in a plastic bag, or ice wrapped by a moist hand towel or washcloth on the tongue.
Ease the pain. Any use of ice will help with immediate pain. You can rotate your use of ice packs for several hours, alternating between 20 minutes on and 20 minutes off. If you tolerate pain medication well, take Tylenol and Advil or Motrin to help with both pain and swelling.
When to See a Doctor
If the above self-care measures do not, especially if you can’t get the bleeding to slow down or stop, get help from a medical professional. Get to an urgent care facility.
Situations that warrant medical attention include:
Excess bleeding: If you sunk your tooth too deep into the tongue, it may be difficult to control the bleeding. A gaping wound may have a similar outcome, requiring surgical sutures to stop the bleeding and facilitate healing.
Severe pain: Your doctor may prescribe mild/moderate pain relievers like oral acetaminophen.
Increasing swelling: Inflammation worsens your pain, and you may need to take an anti-inflammatory painkiller like ibuprofen to manage the problem.
Signs of infection: In very rare cases, a tongue injury may get infected. Fever and swelling two days after the cut may indicate this. Your dentist may prescribe antibiotics to fight any infection.
Canker sores: These should naturally go away in one or two weeks without treatment. If they do not, you should have them looked at by your dentist. Applying a topical solution to the bite site, such as a mouth rinse, can help control the pain and speed up healing.
How Long Will It Take to Heal?
The length of time it takes a tongue bite to heal depends on the severity of the bite. A simple nick will bleed only for a few minutes without any compression, will swell for a day or so, and will be forgotten soon thereafter.
A significant bite requires more care: compression, ice and possible pain meds. Now we’re talking about two to five days of care.
Healing time for a serious bite, such as something that comes from being involved in a car accident or sports injury, can take weeks or longer. That depends if stitches are needed to close the laceration and if doctors begin a regiment of antibiotics to ward off infection.
Why You Repeatedly Bite Your Tongue
Biting your tongue frequently can make life miserable and expose you to bigger health and treatment challenges. If this problem recurs consistently, consider seeing your personal doctor or dentist to get their opinion and recommendations.
Repeated tongue biting can exacerbate otherwise mild oral issues. If you think you might be prone to frequent tongue injury, do not hesitate to see your dentist. Medical professionals will dial in on root causes, such as an abnormal bite, seizures, sleep issues or other physical or lifestyle characteristics that are specific to you.
Prevention
Preventing regular tongue-biting will require action on your part. Either you will need to do some research about when and why you constantly are dealing with this or you’ll need medical help and advice.
Chances are you’re dealing with one of causes listed earlier. Some ways to tackle those causes are to use a mouth guard, wear a tongue protector, take seizure medication or repair a structural issue with your jaw or mouth.
Mouth guards are recommended for many sports, particularly contact sports, as they protect your mouth and tongue from injury. Observe good mouth guard hygiene, including brushing and rinsing the device with cold water after use.
Other people accidentally bite their tongues while they sleep. In these cases, they may need to wear a tongue protector at night. This removable oral device may help people that bite their tongue while sleeping due to teeth grinding or other disorders. Its purpose is to secure the tongue in its natural position in the mouth.
Some people don’t realize it at the time, but they bite their tongue during a seizure and will need seizure treatment If someone’s seizure disorder is manageable with anticonvulsant drugs, they can see a dentist for help preventing tongue-biting.
It would be best to have an orthodontist examine your mouth for dental issues that may contribute to your tongue-biting. Some people with accidental mouth injuries may have jaw misalignment, unfitting dentures, or other oral health issues. Correcting these problems can minimize the occurrence of bit tongues.
Some people bite or chew on their tongue due to stress or anxiety. Mediation exercises, mindful breathing, and relaxation therapies can help to relieve tension in the mouth and face. While it’s not a quick fix, if you incorporate these practices into your daily life, you can reduce stress and reduce the likelihood that you will bite your tongue.
